Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
Definition
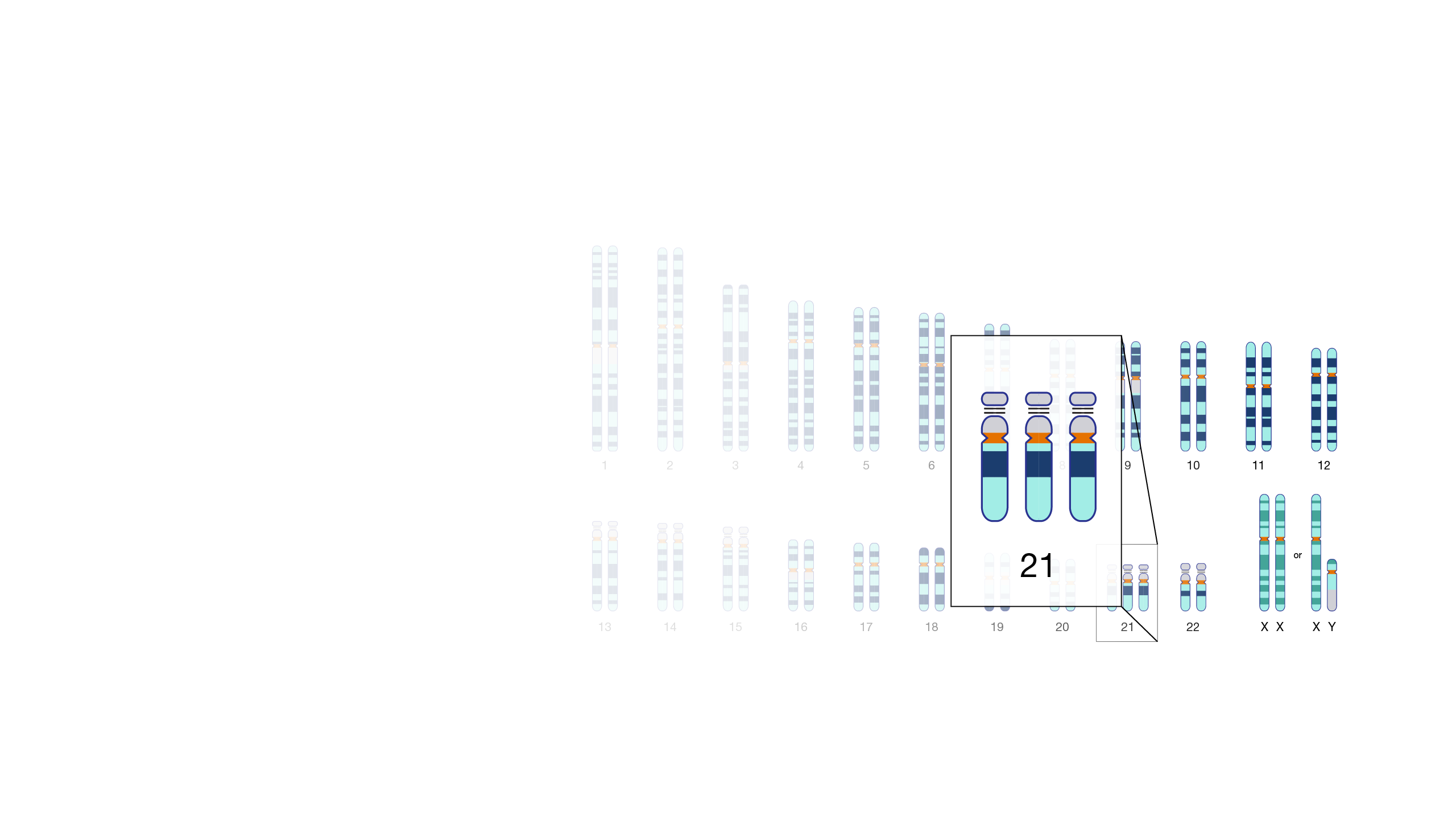
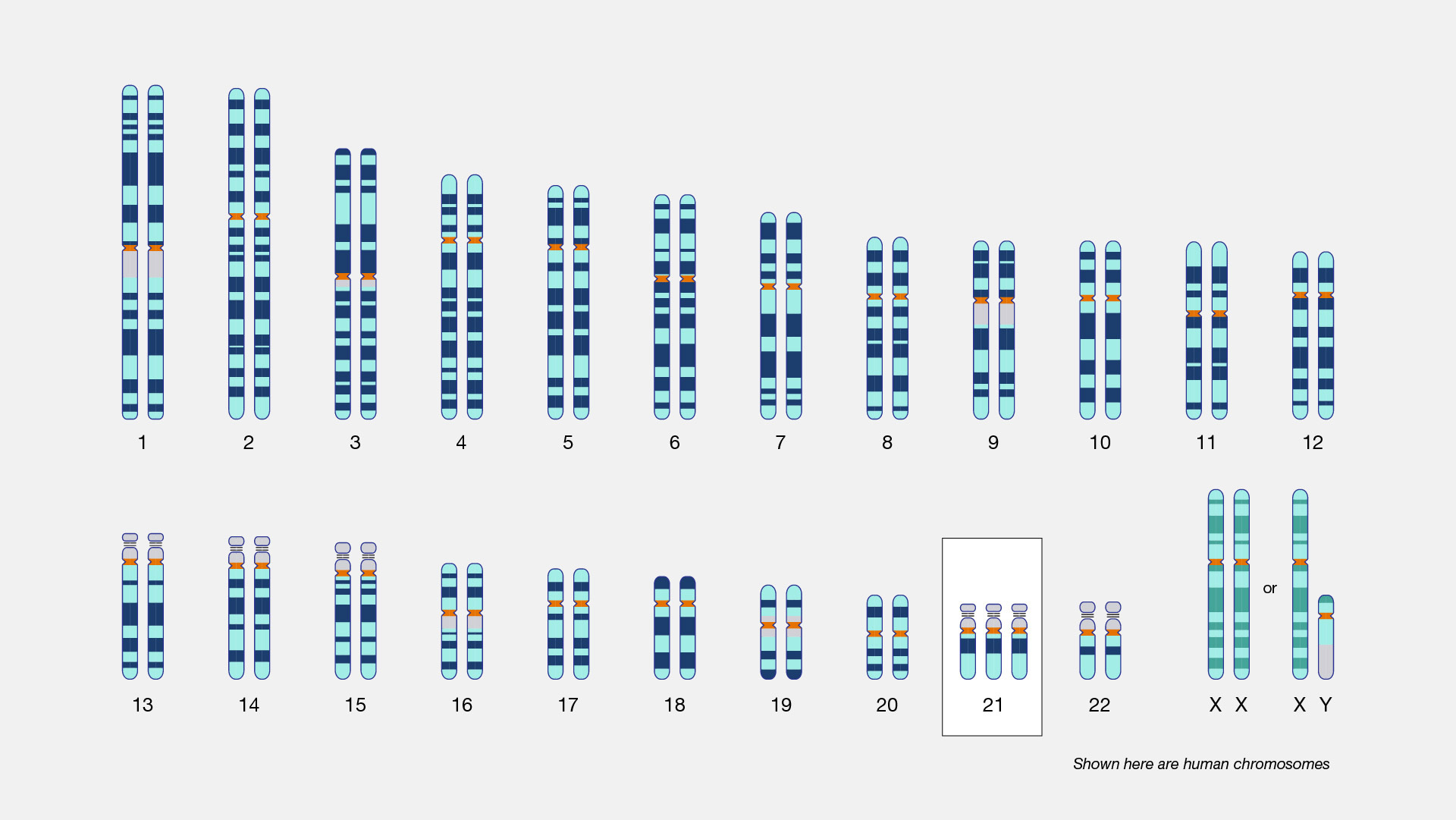
Down syndrome (also called Trisomy 21) is a genetic condition caused by an error in the process that replicates and then divides up the pairs of chromosomes during cell division, resulting in the inheritance of an extra full or partial copy of chromosome 21 from a parent. This extra chromosomal DNA causes the intellectual disabilities and physical features characteristic of Down syndrome, which vary among individuals.
Narration
Down syndrome, trisomy 21. Like all individuals with disabilities, individuals with Down syndrome lead full, autonomous, and enriching lives. From infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and old age, these individuals have many if not most of the same experiences as everyone else. Individuals with Down syndrome, like most people at some point in their lives, may need assistance with certain tasks. They may also have certain health challenges, being more at risk than the typical individual for certain health conditions, all of which are treatable. These individuals are cherished members of each of their communities, going to college, living independently, owning businesses, getting married, and living their lives as they so choose.