Recombinant DNA Technology
Definition
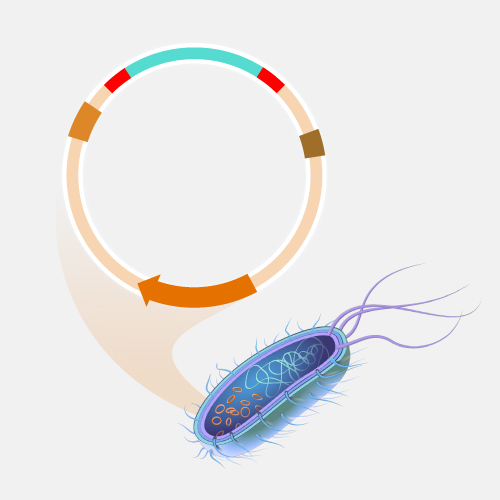
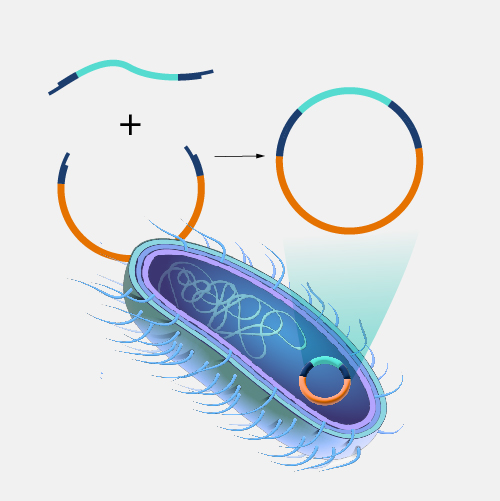
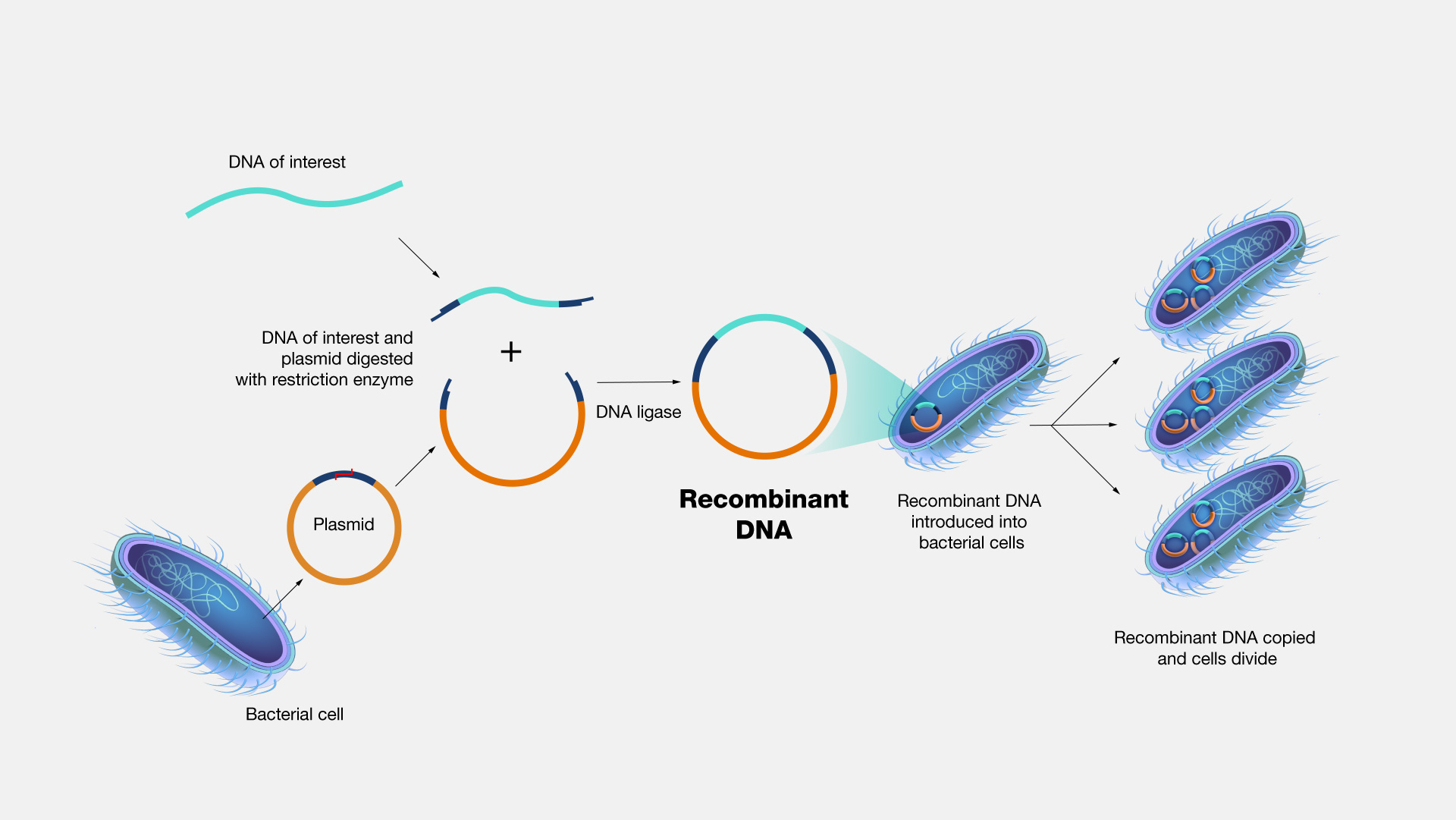
Recombinant DNA technology involves using enzymes and various laboratory techniques to manipulate and isolate DNA segments of interest. This method can be used to combine (or splice) DNA from different species or to create genes with new functions. The resulting copies are often referred to as recombinant DNA. Such work typically involves propagating the recombinant DNA in a bacterial or yeast cell, whose cellular machinery copies the engineered DNA along with its own.
Narration
Recombinant DNA Technology. Recombinant DNA technology is an extremely important research tool in biology. It allows scientists to manipulate DNA fragments in order to study them in the lab. It involves using a variety of laboratory methods to put a piece of DNA into a bacterial or yeast cell. Once in, the bacteria or yeast will copy the DNA along with its own. Recombinant DNA technology has been successfully applied to make important proteins used in the treatment of human diseases, such as insulin and growth hormone.