Translation
Definition
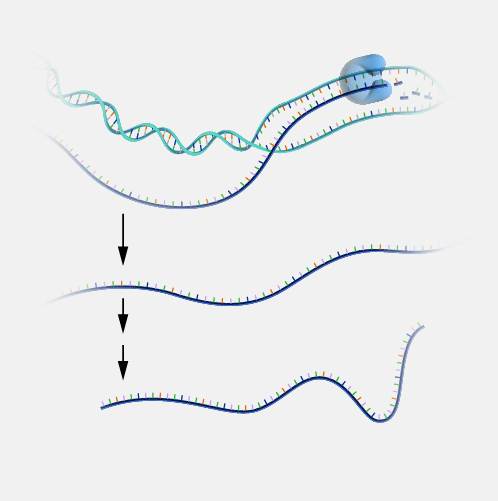
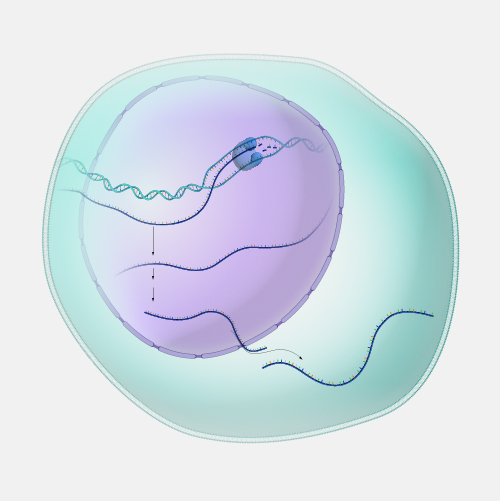
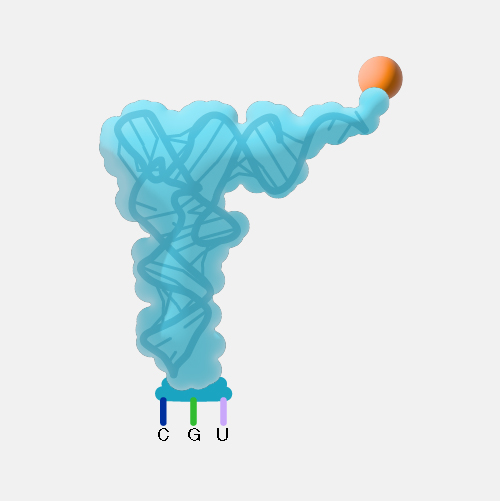
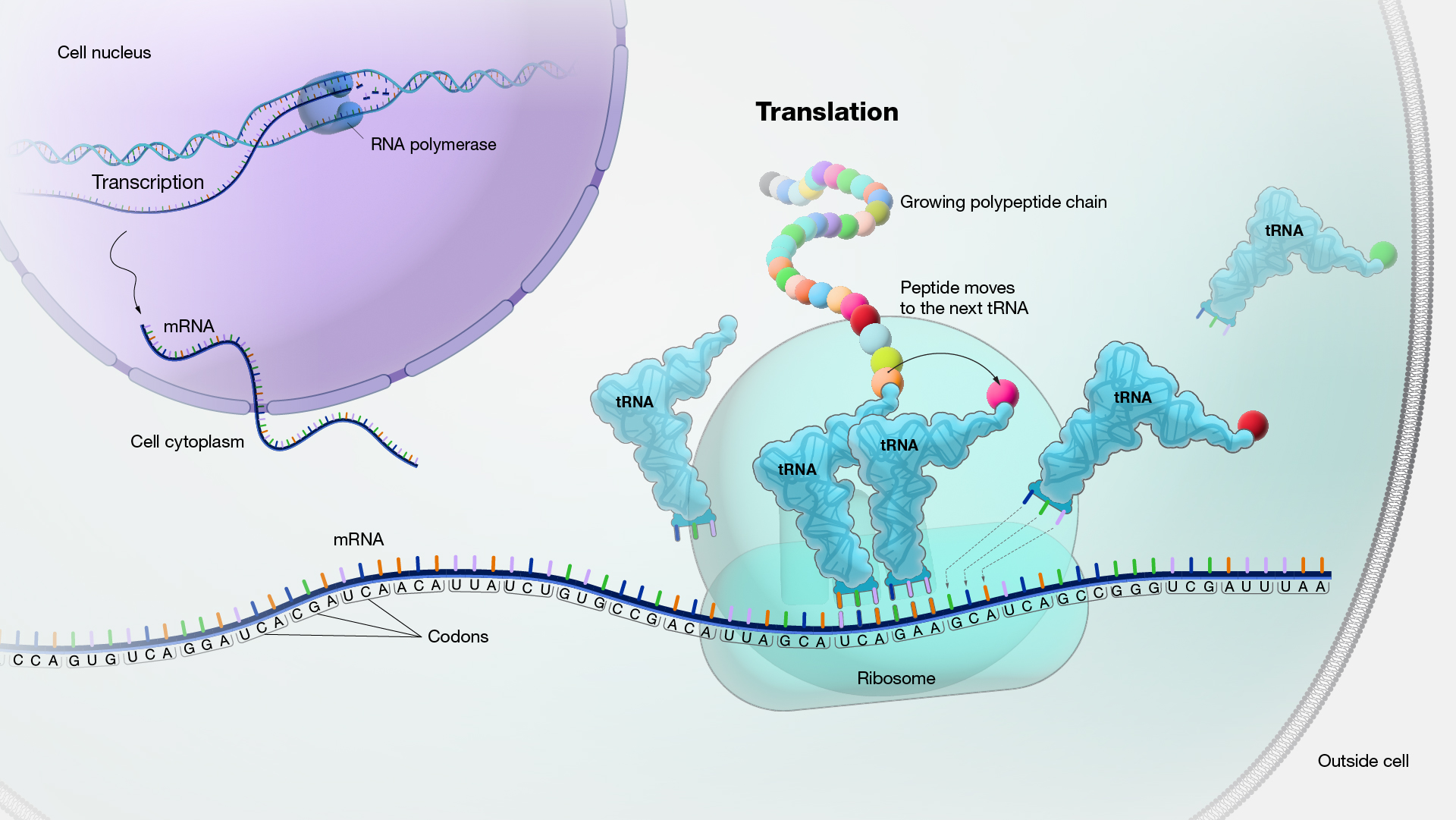
Translation, as related to genomics, is the process through which information encoded in messenger RNA (mRNA) directs the addition of amino acids during protein synthesis. Translation takes place on ribosomes in the cell cytoplasm, where mRNA is read and translated into the string of amino acid chains that make up the synthesized protein.
Narration
Translation. Translation is, perhaps, the single most important event in biology because what protein is translated versus what isn't translated makes the difference between your body building a heart versus lungs.