Translocation
Definition
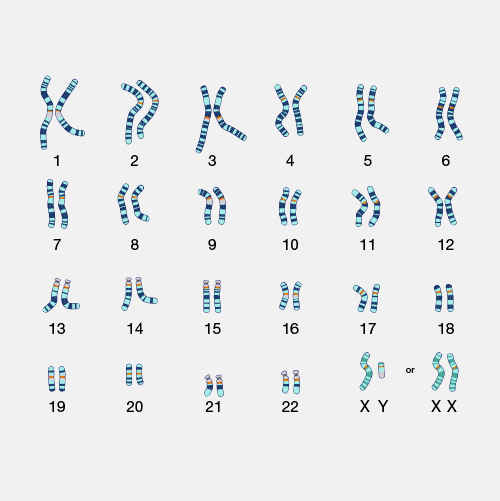
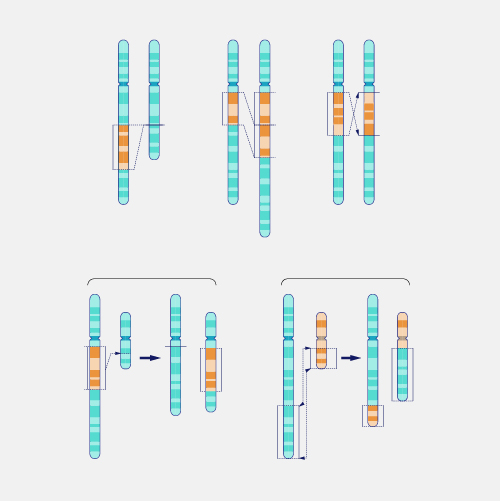
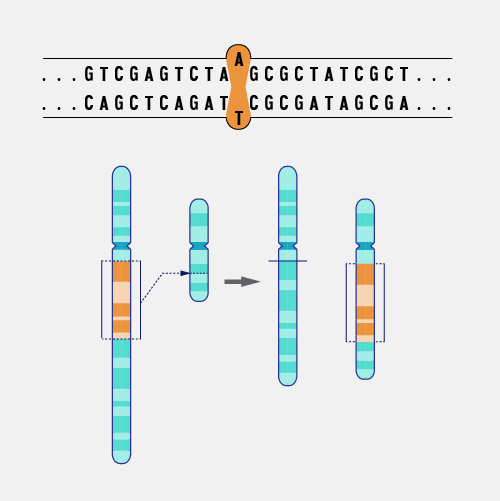
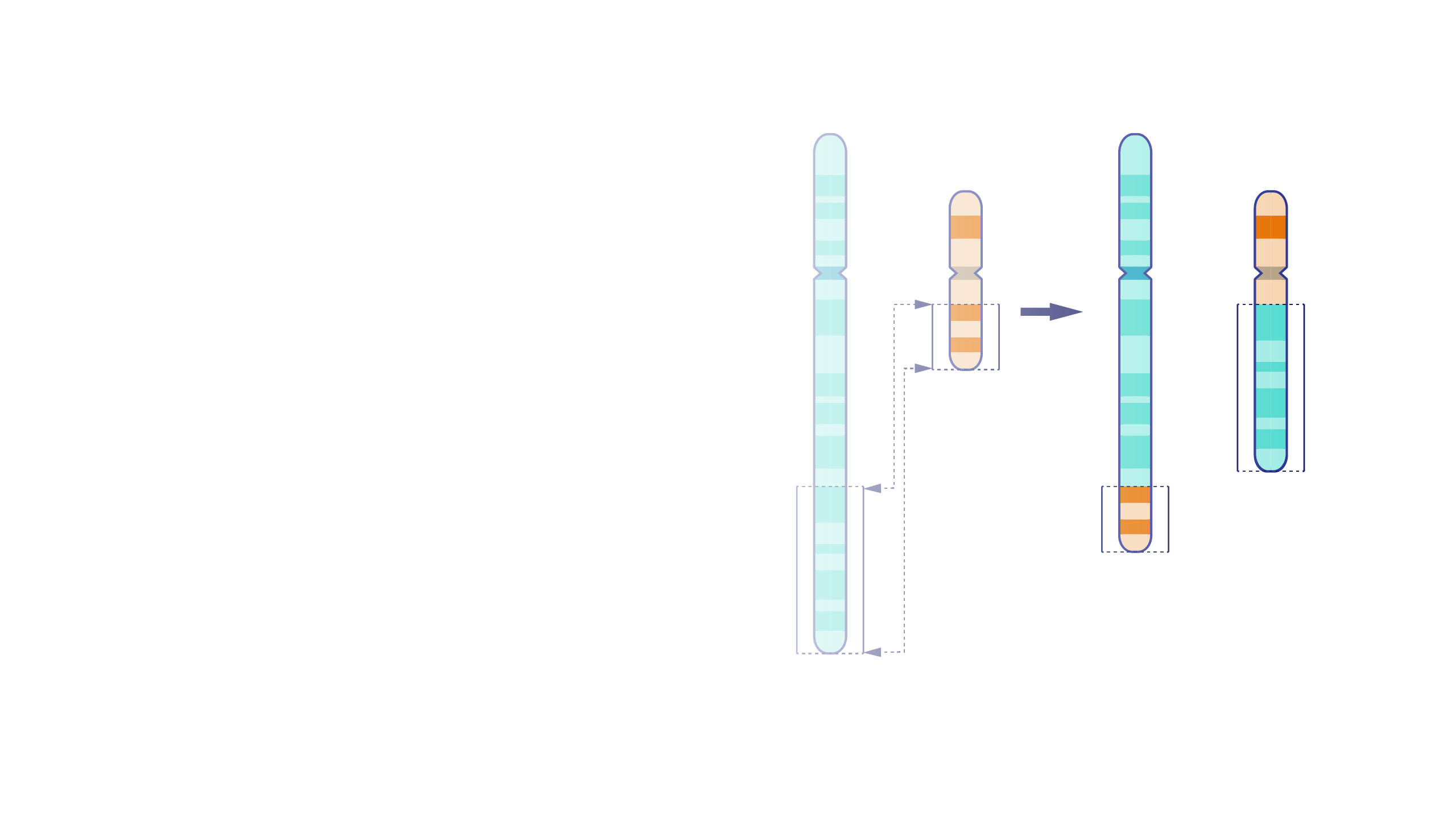
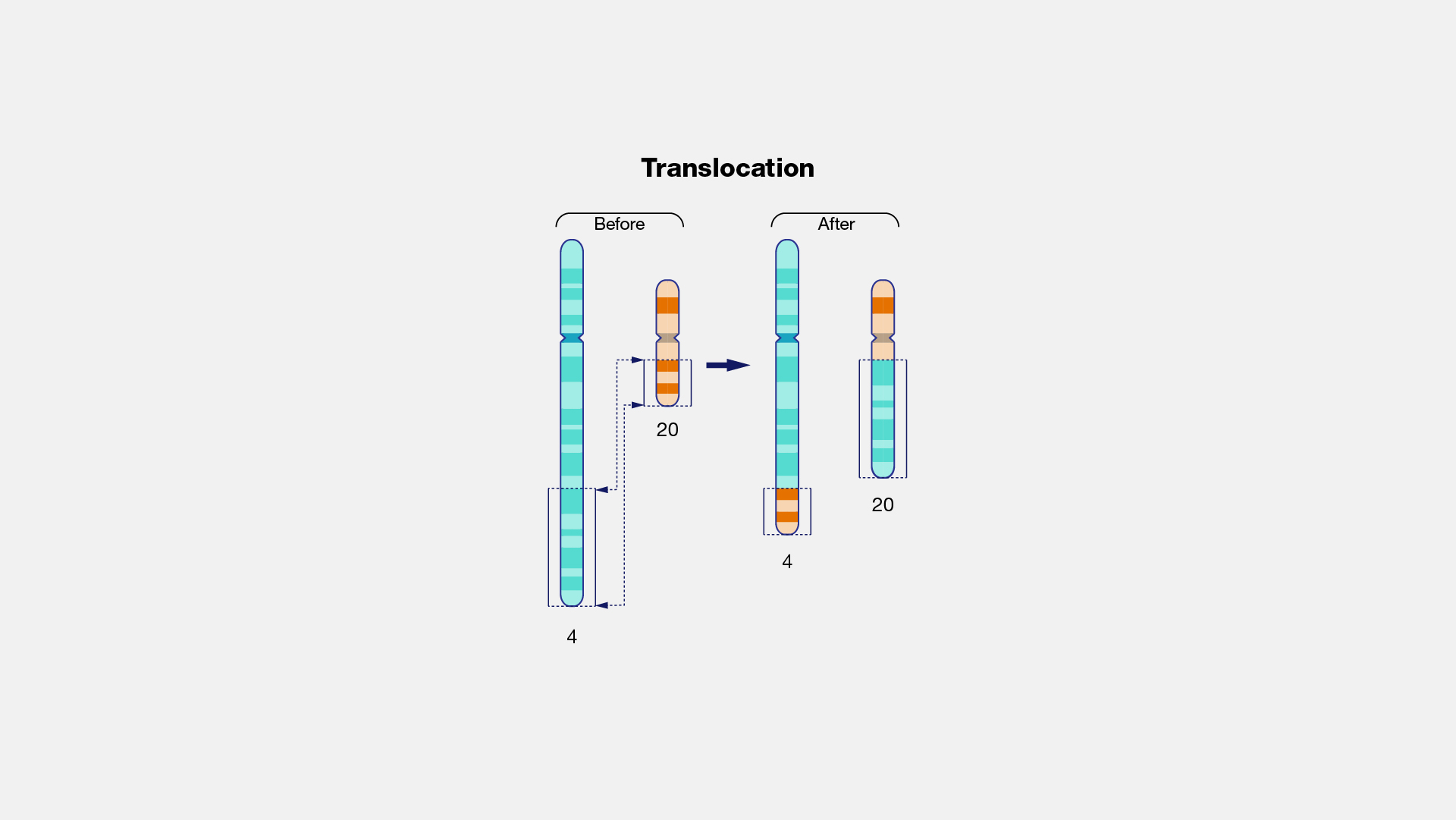
A translocation, as related to genetics, occurs when a chromosome breaks and the (typically two) fragmented pieces re-attach to different chromosomes. The detection of chromosomal translocations can be important for the diagnosis of certain genetic diseases and disorders.
Narration
Translocation. The Philadelphia chromosome is an abnormal chromosome that causes chronic myelogenous leukemia and a subset of other leukemias. It consists of a portion of chromosome 9 fused to a portion of chromosome 22, by a translocation event between these two chromosomes. As a result, the BCR gene is fused to the ABL kinase gene at the site of the translocation. The BCR-ABL gene produces an abnormal hybrid protein. Unlike the normal ABL protein kinase, the hybrid kinase is always turned on and allows chronic myelogenous leukemia cells to grow and survive. Importantly, there are targeted therapies that can turn the hybrid BCR-ABL protein off and kill the cancer cells that contain the Philadelphia chromosome.