Last updated: May 05, 2015
May 5 2015 Genome Wide Association Studies Catalog
Genome-Wide Association Studies Catalog
May 5, 2015
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have proven to be effective for identifying and understanding the genetics underlying human health and disease. The GWAS approach takes advantage of high-throughput DNA analysis methods to examine common genomic variants across human genomes; the goal is to find the variants associated with particular diseases or traits. Once detected, scientists can further study the variants (or variants nearby) to determine their role, if any, in causing disease or influencing the relevant trait.
NHGRI launched the Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) Catalog in 2008 to capture information about published GWAS efforts and to create a curated, downloadable, and user-friendly data resource. The GWAS Catalog started as a series of tables that evolved into a database and the now-iconic chromosome-based graphic seen below. In 2010, NHGRI began a fruitful collaboration with the European Molecular Biology Laboratory-European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), in the U.K., to improve the Catalog experience through additional curation, automated updating, and enhanced search capabilities. Very recently, the GWAS Catalog moved to the EMBL-EBI, but will continue to be curated jointly by EMBL-EBI and NHGRI staff.
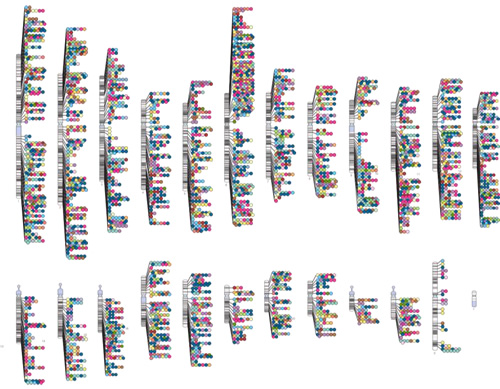 |
To manage and maintain a high-quality data set, Catalog curators developed specific inclusion criteria. Studies must assay a minimum number of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), a type of genomic variant, and include SNP-trait associations that achieve a certain level of statistical significance. The database is highly functional, with an interactive graphic and facile search functions. Users can search the Catalog based on different attributes (e.g.,author, gene, and SNP) and traits (e.g., cancer, diabetes, and obesity).
The real power of the GWAS Catalog lies in its utility. It is gratifying to see researchers incorporate the GWAS Catalog into other genomic resources and use the data to further research studies. GWAS Catalog data have been incorporated into a number of genome browsers, including dbSNP, UCSC, and Ensembl. It has also spawned the development of the Phenotype-Genotype Integrator (PheGenI), a resource developed with NCBI to link GWAS Catalog data with other NCBI databases. NHGRI's Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) Project utilized the GWAS Catalog to identify regulatory elements associated with human disease.
 The GWAS Catalog continues to be a valuable resource for information regarding the vast number of findings coming out of GWAS. With the last data release on May 2, 2015, the GWAS Catalog contained 2,154 published studies and reported information about 15,333 SNPs. The GWAS Catalog graphic has become an iconic image that I see often used to represent the progress made in common disease-associated variant discovery. NHGRI and EBI are committed to maintaining this resource as it continues to grow and serve the research community. To access the GWAS Catalog, see ebi.ac.uk/gwas/. Additional information is available at the NHGRI's GWAS web page: genome.gov/gwastudies/.
The GWAS Catalog continues to be a valuable resource for information regarding the vast number of findings coming out of GWAS. With the last data release on May 2, 2015, the GWAS Catalog contained 2,154 published studies and reported information about 15,333 SNPs. The GWAS Catalog graphic has become an iconic image that I see often used to represent the progress made in common disease-associated variant discovery. NHGRI and EBI are committed to maintaining this resource as it continues to grow and serve the research community. To access the GWAS Catalog, see ebi.ac.uk/gwas/. Additional information is available at the NHGRI's GWAS web page: genome.gov/gwastudies/.
