The Model Organism Databases and Gene Ontology (GO) Consortium resources serve as well-curated authoritative genomic compendia of diverse model organism annotations to catalyze progress in human genome research and support its translation into clinical utility. Annotations include gene function, phenotypic alleles and variants, human disease associations, pathways, gene expression, and both protein–protein and genetic interactions. Given the significant use of these resources, NHGRI aims to improve the interoperability of these resources to facilitate more holistic and effective use of the information in these resources. In collaboration with these resources and the broader NIH community another important goal has been to develop a sustainable approach that also facilitates economical and efficient means to remain at the forefront of implementing the latest innovative technologies to seize new opportunities for improvements. These goals are in alignment with the steps for modernizing the NIH data resources ecosystem which are outlined in the NIH Strategic Plan for Data Science.
In accordance with these goals the Alliance of Genome Resources (Alliance) was established in September 2016 as a one-stop-shop resource to allow integrated access to the knowledge from these resources. Its centralized component allows for a “develop once, use by all” approach for data types common across model organisms, while the federated knowledge centers are aligned through their “common mission, different paths” with focus on standards to unify data and knowledge. This leads to harmonized curated data which allows researchers to efficiently access the knowledge.
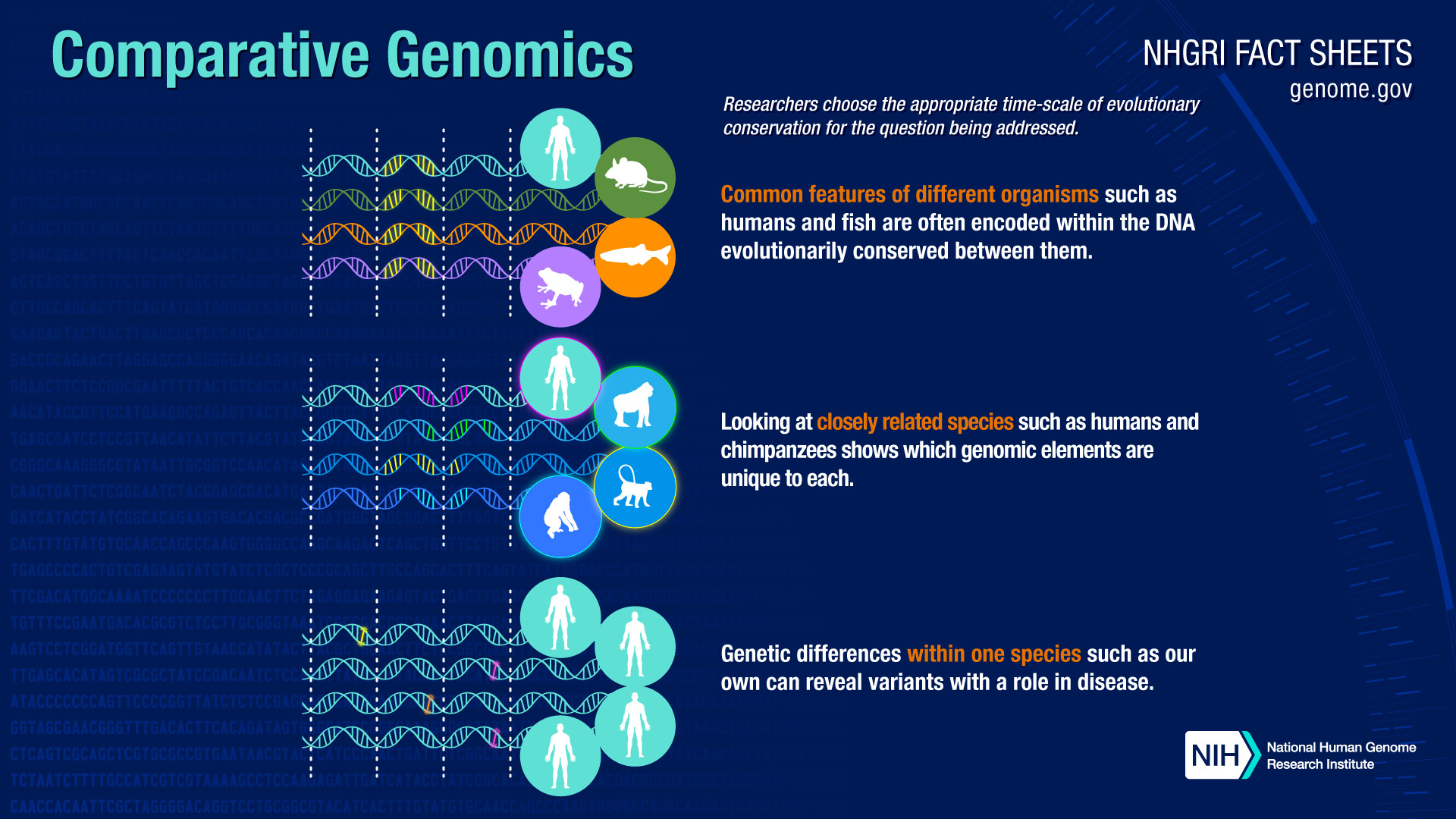
Adoption of shared up-to-date best practices and technologies for activities such as curation, software development and data-management is facilitating novel ways of integrated access, visualization, and analysis of knowledge in these resources. The modular infrastructure allows it to serve as an extensible “knowledge commons” to accommodate additional model organisms. The Alliance has enhanced the ability of researchers to easily compare biological annotations for common data types across model organisms and human through the implementation of shared programmatic access mechanisms, data-specific web pages with a unified “look and feel,” and interactive user interfaces specifically designed to support comparative biology. It is enabling comparative genomics across multiple species in the MODs which is improving the use of model systems to investigate the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying human biology and disease and to translate mechanistic insights from studies in model organisms for clinical applications. The full mission and vision can be viewed on the Alliance website.
Governance
The Alliance has a Scientific Advisory Board (SAB) with representatives selected by the Alliance grantees from the appropriate advisory groups of the individual MODs. To-date, six NHGRI-funded MODs/data resources namely, the Mouse Genome Database (MGD), WormBase, Zebrafish Information Network (ZFIN), Saccharomyces Genome Database (SGD), FlyBase, and the Gene Ontology (GO) Consortium, the NHLBI-funded Rat Genome Database (RGD) and the NICHD-funded Xenbase
The Alliance was recognized as a Global Core Biodata Resource in 2022.