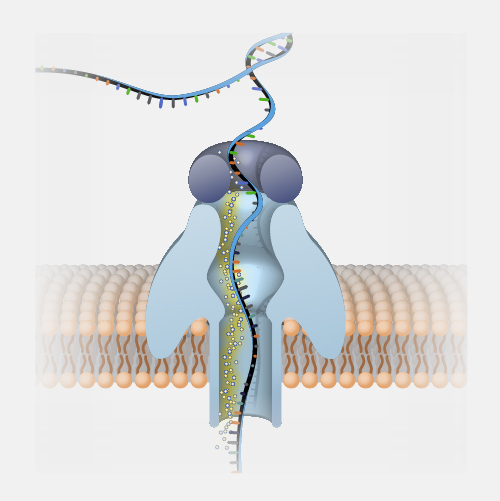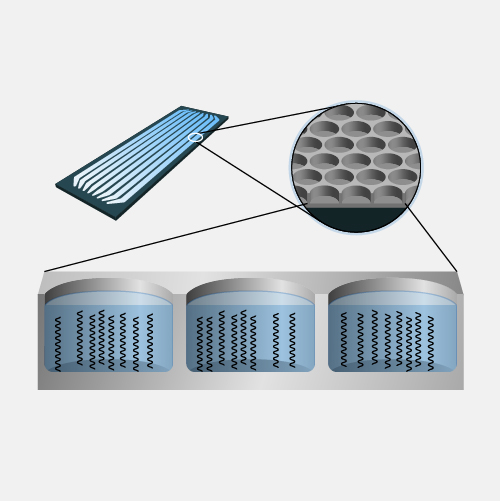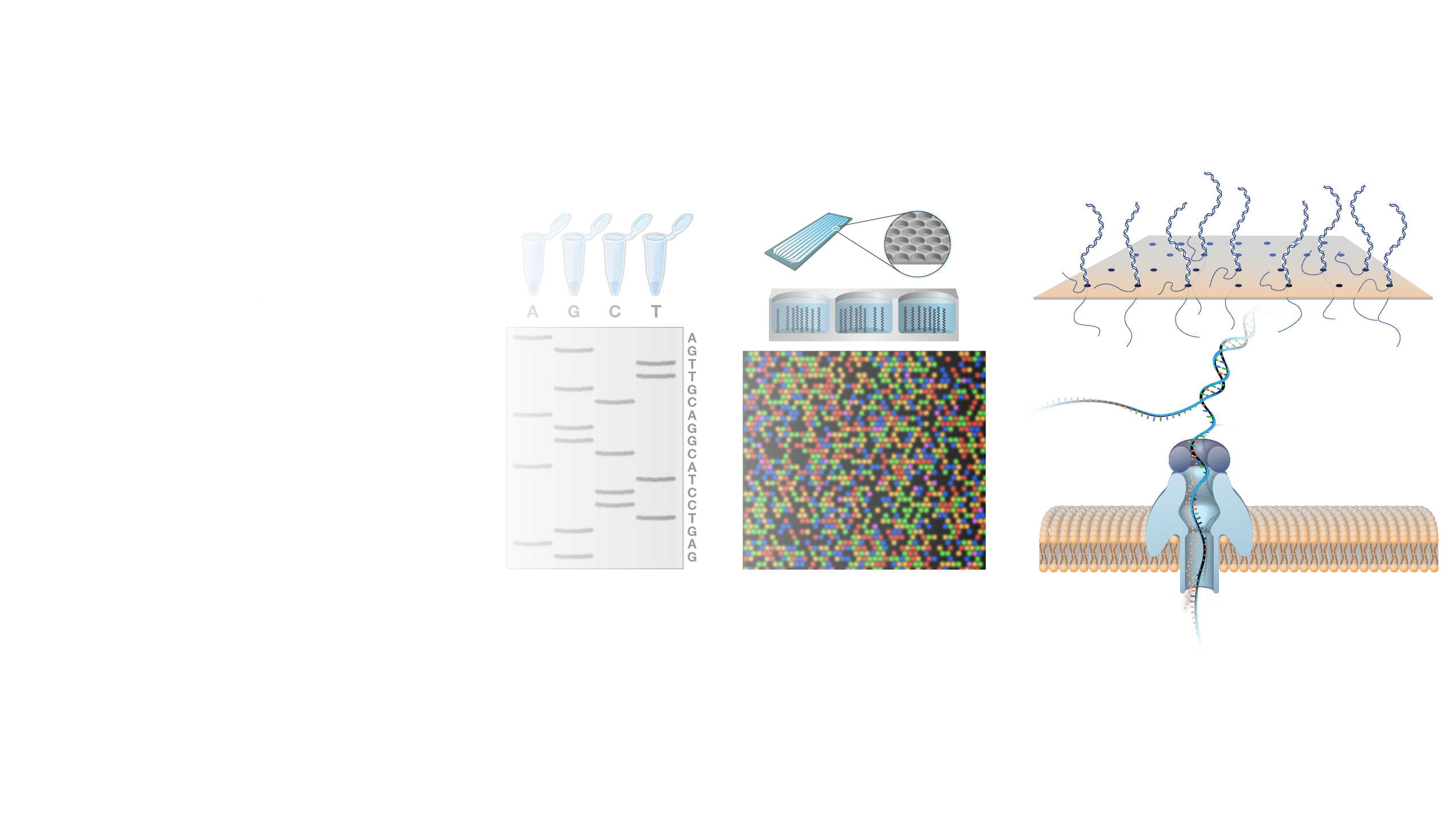
DNA Sequencing
Definition
DNA sequencing refers to the general laboratory technique for determining the exact sequence of nucleotides, or bases, in a DNA molecule. The sequence of the bases (often referred to by the first letters of their chemical names: A, T, C, and G) encodes the biological information that cells use to develop and operate. Establishing the sequence of DNA is key to understanding the function of genes and other parts of the genome. There are now several different methods available for DNA sequencing, each with its own characteristics, and the development of additional methods represents an active area of genomics research.
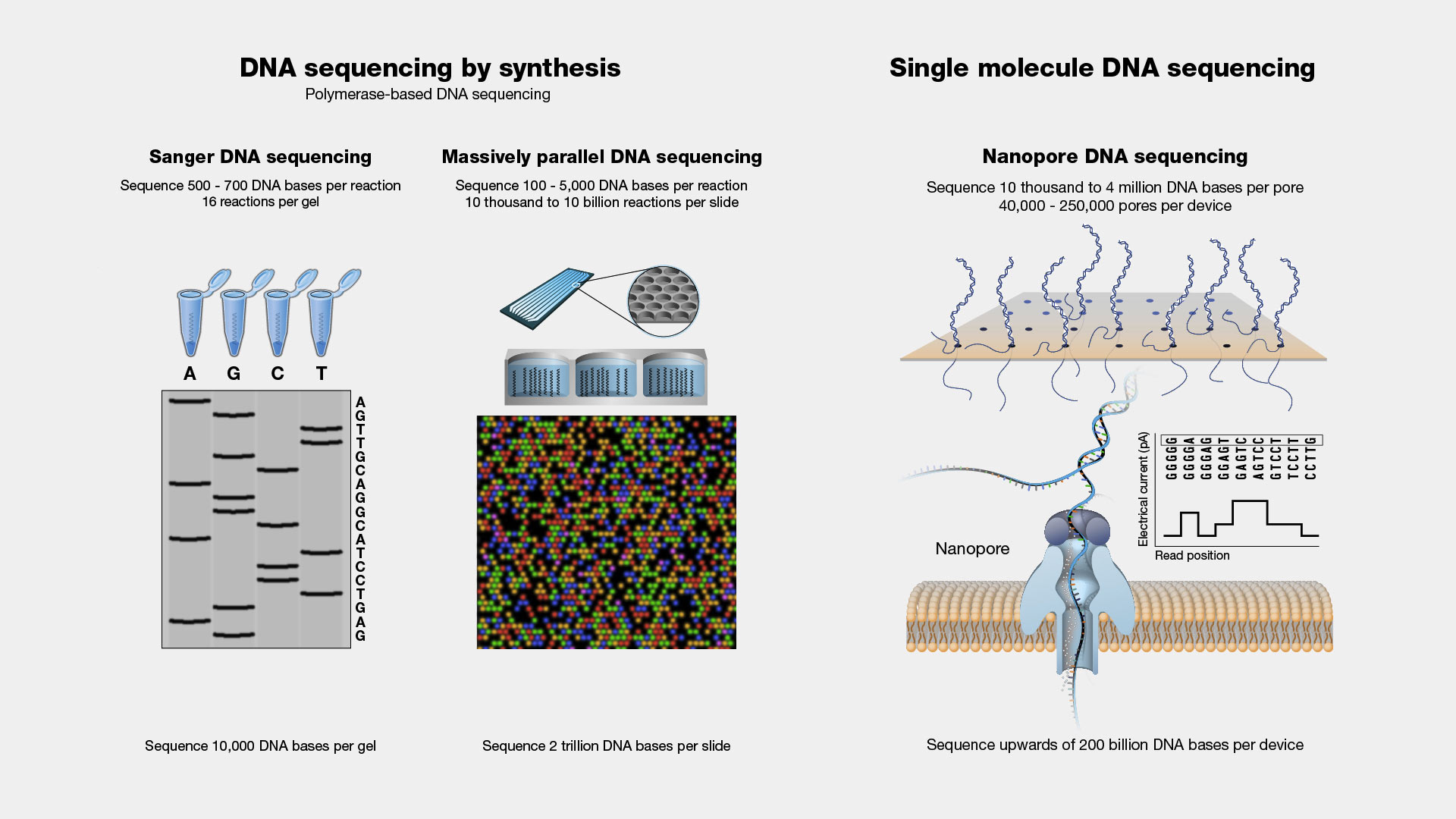
Narration
DNA Sequencing. In terms of information, DNA is like printed text. There is a method of storing the data (the printed word), a language to learn, and a process of understanding the meaning of what has been written. DNA sequencing is a process of reading. In the past, few people could read, most were illiterate. The expansion of literacy has meant that written information is accessible to a large group of people for interpretation, study, and communication. Advances in technology in our more recent history have had a similar effect on the human genome. Reading DNA through DNA sequencing has expanded access to the information in our genomes. The ongoing challenge going forward will be to expand understanding about what this information means for our health.